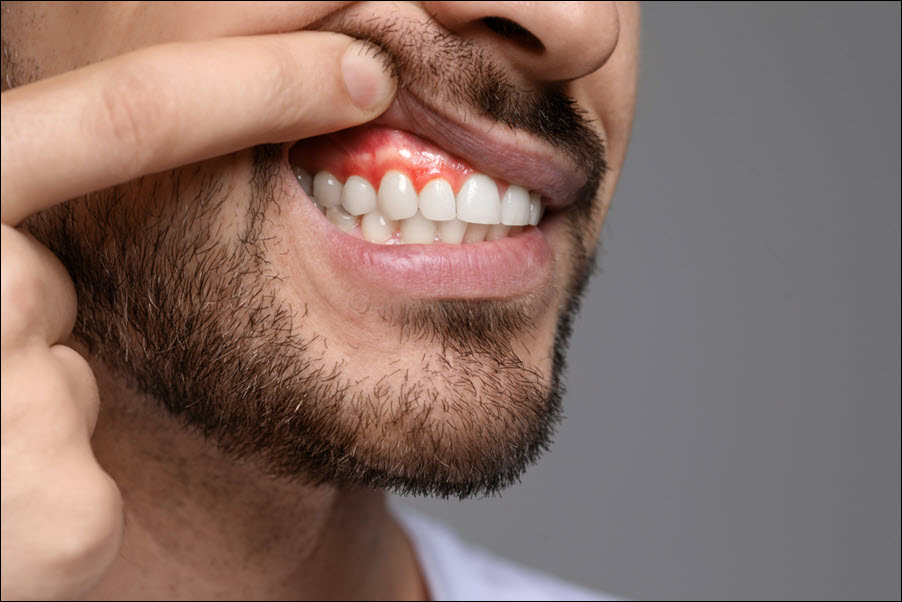
Gingivitis is the early stage of gum disease caused by plaque buildup along the gumline. It leads to red, swollen, and bleeding gums. Poor oral hygiene, smoking, and certain health conditions increase the risk of gingivitis. Early detection and treatment prevent it from progressing to periodontitis, which causes tooth loss and bone damage. Brushing, flossing, and regular dental checkups reduce plaque and strengthen gum health. Treating gingivitis improves gum strength and reduces inflammation. Understanding the signs, prevention methods, and treatments helps protect your gums and improve overall oral health. Let’s explore how to prevent, identify, and correct gingivitis effectively.
How to Prevent Gingivitis
 Brushing and flossing daily prevent plaque buildup and gum inflammation. Plaque forms within 24 hours of eating and hardens into tartar if not removed. Brush twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and a soft-bristled toothbrush. Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles between teeth. Use an antibacterial mouthwash to kill bacteria and reduce plaque. Eating a balanced diet strengthens gum tissue and reduces inflammation. Avoid smoking and tobacco use, which weaken gums and increase plaque buildup. Regular dental cleanings remove tartar and improve gum health. Stronger gums resist infection and improve overall dental comfort. Consistent oral hygiene prevents gingivitis and protects long-term gum health.
Brushing and flossing daily prevent plaque buildup and gum inflammation. Plaque forms within 24 hours of eating and hardens into tartar if not removed. Brush twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and a soft-bristled toothbrush. Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles between teeth. Use an antibacterial mouthwash to kill bacteria and reduce plaque. Eating a balanced diet strengthens gum tissue and reduces inflammation. Avoid smoking and tobacco use, which weaken gums and increase plaque buildup. Regular dental cleanings remove tartar and improve gum health. Stronger gums resist infection and improve overall dental comfort. Consistent oral hygiene prevents gingivitis and protects long-term gum health.
Signs and Symptoms of Gingivitis
Red, swollen, and tender gums signal early-stage gingivitis. Bleeding while brushing or flossing indicates gum inflammation and weakened tissue. Persistent bad breath (halitosis) results from bacterial buildup along the gumline. Gums that appear shiny or recede from the teeth signal gum damage. Increased tooth sensitivity to hot and cold foods also indicates enamel and gum weakening. Pain or discomfort while chewing reflects underlying gum inflammation. Gingivitis often starts painlessly, making early signs easy to overlook. Dentists diagnose gingivitis by measuring gum pocket depth and checking for plaque buildup. Early detection improves treatment success and prevents complications. Recognizing symptoms early increases the chances of complete recovery.
Professional Treatment for Gingivitis
Professional dental cleanings remove plaque and tartar buildup beneath the gumline. Dentists use ultrasonic tools to break up hardened tartar. Scaling and root planing smooth the tooth roots and remove bacteria from gum pockets. Deep cleaning reduces gum inflammation and improves gum attachment to the teeth. Dentists may apply antibiotic gel to reduce infection and speed healing. Improved gum health strengthens tooth stability and reduces sensitivity. Professional fluoride treatments strengthen enamel and protect against future plaque buildup. Dentists also recommend improved brushing and flossing techniques. Regular follow-ups ensure proper gum healing and long-term protection. Early treatment prevents progression to periodontitis and tooth loss.
Home Care for Treating Gingivitis
Brushing and flossing daily reduce plaque and gum inflammation. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste for gentle cleaning. Floss carefully to avoid damaging sensitive gum tissue. Rinse with an antibacterial mouthwash to reduce bacteria and freshen breath. Applying a warm saltwater rinse reduces swelling and discomfort. Eating crunchy fruits and vegetables, like apples and carrots, stimulates saliva and cleans teeth naturally. Drinking more water improves saliva production and reduces plaque buildup. Avoid sugary and acidic foods that weaken enamel and irritate gums. Consistent home care reduces inflammation and improves gum strength. Proper hygiene supports long-term gum health and comfort.
When to Seek Dental Care
Persistent gum inflammation, bleeding, and sensitivity require professional evaluation. Untreated gingivitis progresses to periodontitis, leading to bone loss and tooth damage. If gums pull away from teeth or form deep pockets, seek dental care immediately. Pus between teeth and gums signals infection and requires treatment. Loose teeth reflect advanced gum damage and require prompt correction. Dentists treat advanced gingivitis with deep cleaning, medication, and gum grafting. Early treatment prevents tooth loss and improves gum health. Consistent dental checkups allow early detection and treatment of gum problems. Prompt care increases the chances of full recovery and long-term gum strength.
Maintaining Healthy Gums Long-Term
Regular dental checkups prevent gingivitis and improve gum health. Dentists recommend cleanings every six months to control plaque and tartar buildup. Brushing and flossing daily maintain gum strength and reduce inflammation. Using an antibacterial mouthwash reduces plaque and improves breath freshness. Eating nutrient-rich foods strengthens gum tissue and improves immune response. Staying hydrated increases saliva production, which protects against plaque and decay. Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol use reduces gum irritation and improves healing. Wearing a mouthguard during sleep reduces grinding and protects gums. Consistent care strengthens gums and prevents future infections. Healthy gums support stronger teeth and better overall oral health.
Gingivitis causes gum inflammation, bleeding, and sensitivity. Poor oral hygiene and plaque buildup increase the risk of infection and gum disease. Early signs include red, swollen, and bleeding gums. Brushing, flossing, and using mouthwash prevent plaque buildup and strengthen gum health. Professional dental cleanings remove tartar and improve gum attachment. Early treatment reduces inflammation and prevents progression to periodontitis. Home care, including proper hygiene and diet, supports long-term gum strength. Regular dental checkups ensure early detection and treatment. Investing in gum health prevents tooth loss and improves overall dental comfort. Healthy gums create a stronger, more confident smile.